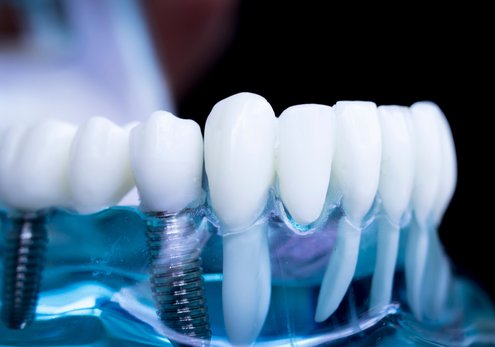
Implant Crowns & Bridges
Reconstruction of missing teeth with implants is currently the most modern solution that allows you to obtain aesthetically and functionally teeth corresponding to your own natural teeth.
Read more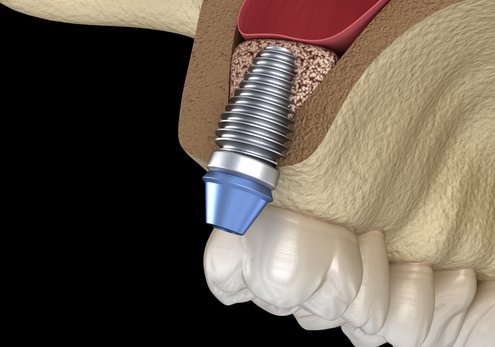
Sinus Lift
Lifting the floor of the maxillary sinus is a procedure that allows the implant to be placed when there is not enough bone separating the oral cavity from the air space of the sinus.
Read more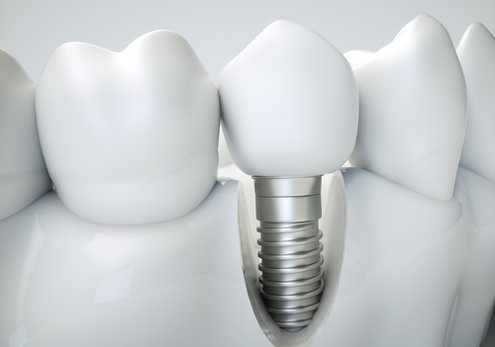
Augmentation - Controlled Bone Regeneration
These treatments aim to surgically produce or reconstruct bone tissue in the place where the dental implants are planned to be placed.
Read moreOffer
Warszawa Ochota
Adres:
ul. Dorotowska 9
02-347 Warszawa
Telefon: +48 501 328 772
E-mail: recepcja@ddclinic.pl
Godziny otwarcia:
Poniedziałek - Piątek: 9:00 - 20:00
Sobota: nieczynne
Warszawa Ursynów
Adres:
ul. Migdałowa 10 lok.5
02-796 Warszawa
Telefon: +48 502 070 050
E-mail: recepcjaursynow@ddclinic.pl
Godziny otwarcia:
Poniedziałek - Piątek: 12:00 - 20:00
Sobota: nieczynne
